Deception on Social Media Platform & Examples of Deception on Social Media
Completion requirements
Types of Deception on Social Media
Introduction
In the first section, we are going to look at understanding the concept of deception on social media platforms.
Social media platforms have fundamentally altered how we interact, exchange information, and understand global events. While these platforms have democratized information access and fostered global communication, they have also given rise to new challenges, particularly the spread of deception. This deception can range from benign misinformation to harmful disinformation, each with distinct characteristics and impacts. Understanding these forms of deception and their implications is crucial for navigating the modern digital landscape.
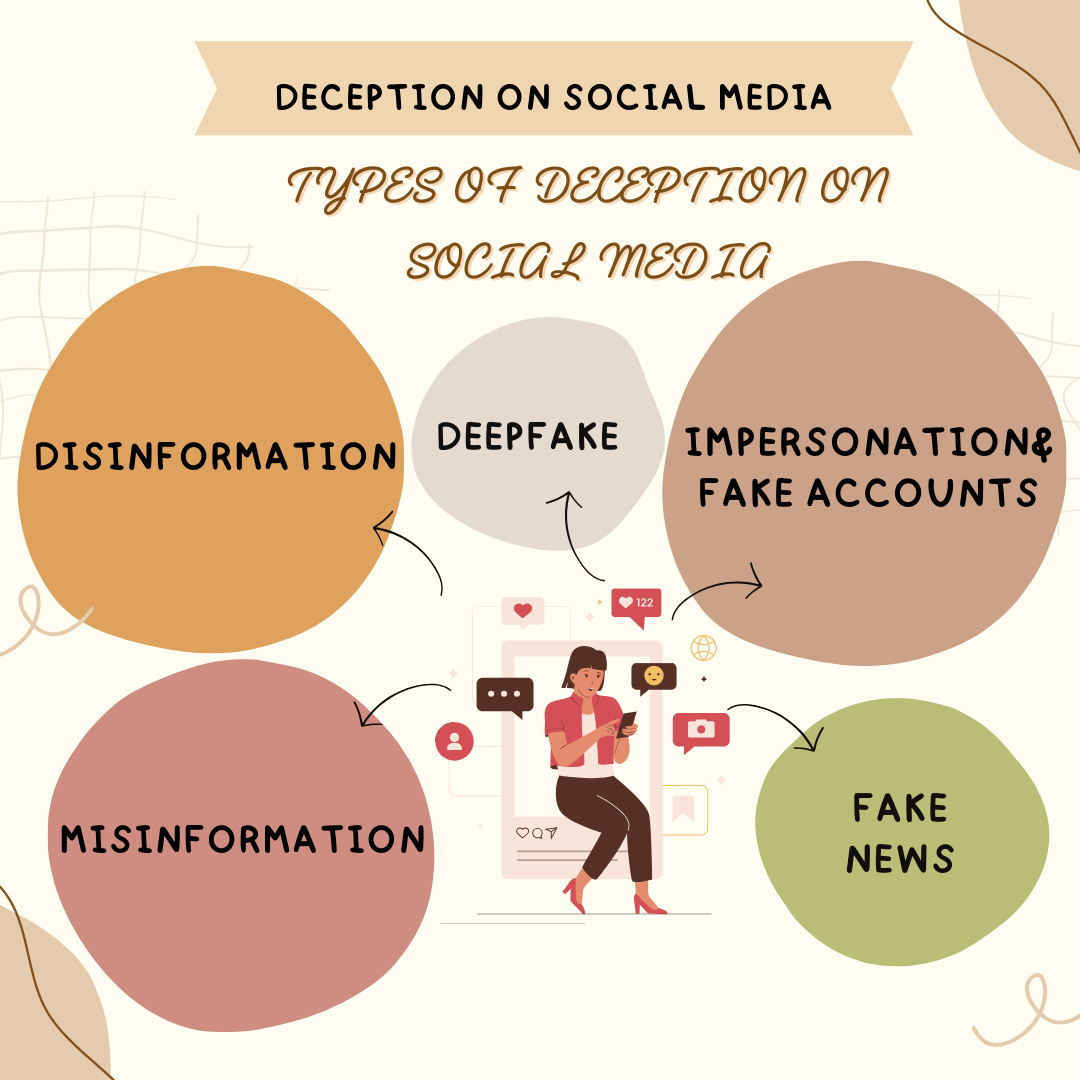
Types of Deception on Social Media
MISINFORMATION
Definition and Nature:
Misinformation involves the sharing of incorrect or misleading information, often without intent to deceive. It can result from errors, misunderstandings, or outdated data. Unlike disinformation, which is deliberately crafted to mislead, misinformation usually arises from honest mistakes or miscommunication.
Impact:
DISINFORMATION
Definition and Nature:
Disinformation refers to the intentional creation and spread of false information to deceive others. This can be driven by political motives, financial gain, or other strategic objectives. Disinformation campaigns are often well-coordinated and designed to manipulate opinions or create division.
Impact:
Disinformation can severely undermine trust in institutions and exacerbate societal divides. For example, during elections, disinformation campaigns might spread false claims about candidates or voting processes, influencing voter behavior and undermining democratic processes. The intent is to sway public opinion or disrupt electoral integrity.
FAKE NEWS
Definition and Nature:
Fake news consists of entirely fabricated stories presented as legitimate news. These stories are designed to attract attention and drive engagement, often by exploiting sensationalism or emotional appeals. Fake news can be spread through social media platforms, news aggregators, or websites posing as credible news sources.
Impact:
The spread of fake news can distort public perceptions and influence behavior based on false premises. For example, a fabricated news story claiming that a celebrity endorsed a controversial product can mislead consumers and impact their purchasing decisions. The sensational nature of fake news often leads to rapid and widespread dissemination, magnifying its effects.
DEEP FAKES
Definition and Nature:
Deepfakes use artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to create hyper-realistic but fake audio or video content. These synthetic media can convincingly depict people saying or doing things they never actually did. Deepfakes exploit advances in technology to produce content that is difficult to distinguish from reality.
Impact:
IMPERSONATION AND DEEPFAKES
Definition and Nature:
Impact:
Now lets watch a video about the examples of deception on social media.
Examples of Deception on social media .mp4
Last modified: Wednesday, 18 September 2024, 3:36 PM
